The training was perfect. Great slides. Clear demonstrations. Everyone nodded along.
A week later, no one is using the tool.
What happened? Training happened. Learning didn't.
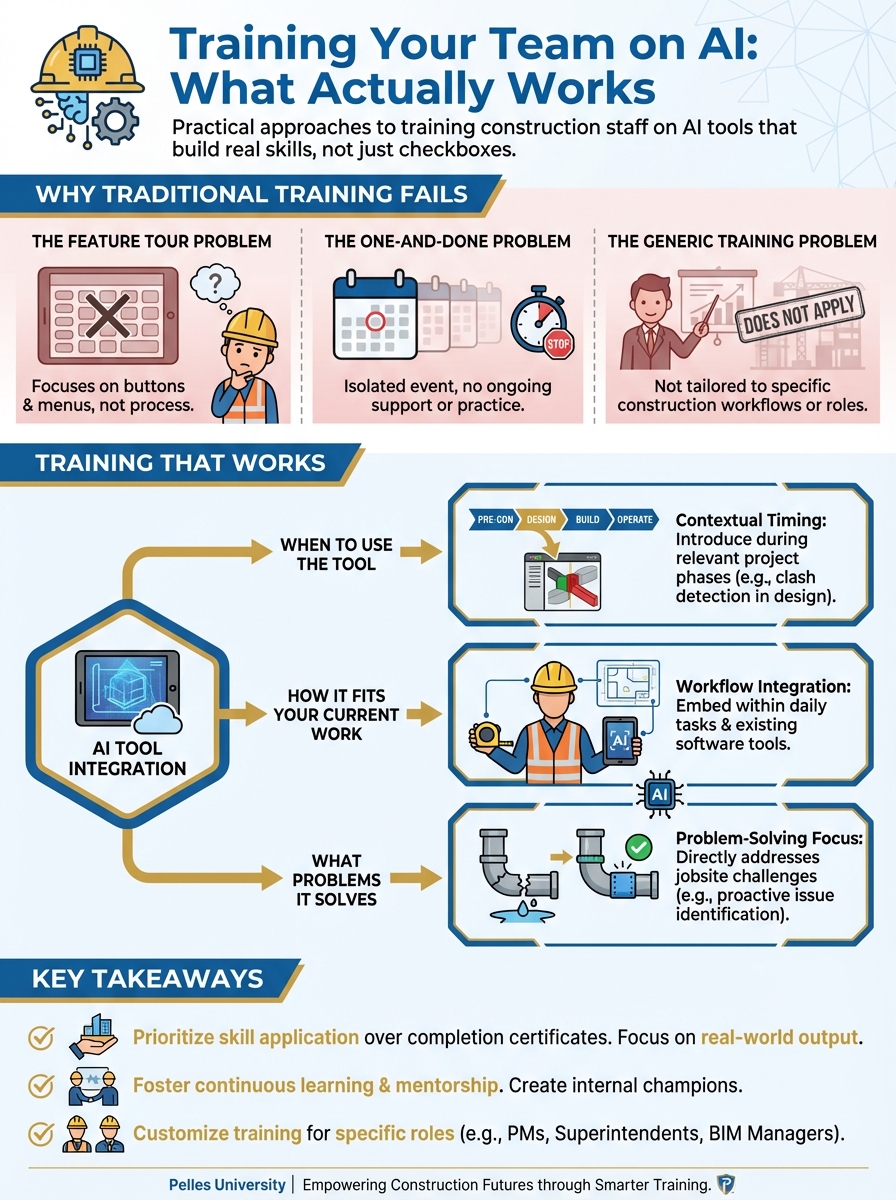
Why Traditional Training Fails
The Feature Tour Problem
Typical training: "Here's the menu. Here's where you click to upload. Here's the settings panel."
This teaches features. It doesn't teach:
- When to use the tool
- How it fits your current work
- What problems it solves
- How to handle unexpected results
Features are forgotten. Workflows are remembered.
The One-and-Done Problem
Training happens once. Then:
- Questions arise with no one to answer
- Obstacles appear with no support
- Old habits return without reinforcement
- Skills decay without practice
Learning requires repetition and support over time.
The Generic Training Problem
Everyone gets the same training:
- Estimators, PMs, and field staff together
- Generic examples, not your projects
- Theoretical scenarios, not your workflows
Irrelevant training doesn't stick.
Training That Works
Principle 1: Workflow-Centered
Train around work tasks, not tool features:
Not: "Here's how to create a query in the AI tool." Instead: "Here's how to find warranty requirements in a spec quickly."
The tool is a means. The work task is the end.
Principle 2: Role-Specific
Different roles need different training:
Estimators:
- Spec review workflows
- Quantity verification
- Pricing analysis
- Bid package triage
Project Managers:
- Contract review
- RFI drafting
- Change order documentation
- Closeout preparation
Field Staff:
- Quick spec lookups
- Safety documentation
- Quality checklist support
Same tool, different applications.
Principle 3: Spaced Learning
Spread training over time:
| Week | Session | Topic |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 min | Core concept + one workflow |
| 2 | 20 min | Second workflow + practice review |
| 3 | 20 min | Third workflow + Q&A |
| 4 | 20 min | Advanced tips + troubleshooting |
Short sessions with practice between beat marathons.
Principle 4: Hands-On Practice
Learning happens by doing:
During training:
- Use real project documents
- Practice actual workflows
- Solve realistic problems
- Make mistakes in safe environment
Ratio: At least 50% of training time should be hands-on.
Principle 5: Ongoing Support
Training is the start, not the end:
Support mechanisms:
- Office hours for questions
- Quick-reference guides
- Peer help network
- Escalation path for issues
Availability matters more than comprehensiveness.
Designing the Training Program
Step 1: Identify Use Cases
Before training, answer:
- What specific tasks will people use AI for?
- What problems are they solving?
- What does success look like?
- How will they know it's working?
Specific use cases guide training content.
Step 2: Build Role-Based Tracks
Create separate tracks by role:
Track 1: Estimators
- Session 1: Spec review for scope development
- Session 2: Analyzing bid requirements
- Session 3: Checking estimates and pricing
- Session 4: Building reusable prompts
Track 2: Project Managers
- Session 1: Contract review basics
- Session 2: RFI and communication drafting
- Session 3: Change order support
- Session 4: Documentation workflows
Tailor content to what each role actually does.
Step 3: Gather Real Materials
Use actual project materials:
- Specifications from recent projects
- Contracts your team has reviewed
- RFIs that have been submitted
- Change orders that were processed
Real materials make training immediately relevant.
Step 4: Create Practice Exercises
Design exercises that mirror real work:
Example exercise for estimators:
Exercise: Spec Review for Mechanical Scope
Using the attached specification sections, identify:
1. All fire stopping requirements for penetrations
2. Equipment warranty requirements
3. Testing and balancing responsibilities
Use the AI tool to help. Verify the results against
the actual spec. Note any discrepancies.
Time: 15 minutes
Exercises should be completable in training time.
Step 5: Develop Support Materials
Create reference materials:
Quick-reference card:
- Common prompts for this role
- Workflow steps
- Where to get help
FAQ document:
- Common questions and answers
- Troubleshooting tips
- Escalation contacts
Video library:
- Short demos of common workflows
- Tips from experienced users
Materials support retention after training.
Delivering Effective Training
Setting the Stage
Start every session by answering:
- Why does this matter for your work?
- What specific problem does this solve?
- What will you be able to do after?
Connect to their reality.
Demonstration First
Show the complete workflow:
- Start with the work task
- Show how AI helps
- Demonstrate the complete process
- Highlight decision points
Let them see success before attempting.
Guided Practice
Walk through together:
- Everyone follows along
- Pause for questions
- Address issues immediately
- Repeat as needed
Supervised practice builds confidence.
Independent Practice
Let them try alone:
- Provide exercise with clear goal
- Circulate to help
- Encourage peer assistance
- Debrief what worked
Independent practice reveals gaps.
Closing Strong
End every session with:
- Recap of key workflow
- Assignment for practice before next session
- Where to get help
- What's coming next
Momentum carries into real work.
Training Different Audiences
Experienced Professionals
Challenges:
- Established workflows they trust
- Skepticism about new tools
- "My way works fine" mindset
- Fear of looking incompetent
Approaches:
- Respect their expertise
- Show how AI enhances, not replaces
- Use their real work examples
- Let results convince them
Sample framing: "You've got 20 years of experience knowing what to look for. AI helps you find it faster so you can spend more time on the judgment calls only you can make."
New Hires
Challenges:
- Learning job and tool simultaneously
- No baseline for comparison
- May not know when AI is wrong
- Dependent on AI without understanding
Approaches:
- Integrate AI into job training
- Teach verification skills
- Build understanding, not just usage
- Pair with experienced mentors
Sample framing: "AI will help you move faster, but you need to understand the work to know when AI is right. Let's build both skills together."
Tech-Skeptical Staff
Challenges:
- Previous bad experiences
- Don't trust technology
- Prefer traditional methods
- May actively resist
Approaches:
- Acknowledge their concerns
- Start with small, low-risk wins
- Show specific value, not general hype
- Don't force—invite
Sample framing: "I know you've seen software come and go. Let's try it on something small. If it doesn't help, no problem. But if it saves you time on [specific pain point], maybe it's worth keeping."
Tech-Enthusiastic Staff
Challenges:
- May skip foundational learning
- Overconfident in AI outputs
- Might miss verification steps
- Could frustrate less-tech-savvy peers
Approaches:
- Channel enthusiasm productively
- Emphasize verification importance
- Train as peer helpers
- Set expectations for helping others
Sample framing: "You're picking this up quickly. As you get comfortable, I'd like you to help others who are learning. Teaching will deepen your own skills."
After Training: Making It Stick
Immediate Application
The biggest predictor of retention:
Use the skill within 24 hours
Plan training timing so real work follows immediately.
Office Hours
Regular availability for questions:
- Weekly 30-minute drop-in session
- No agenda—bring your questions
- Solve real problems
- Build confidence
Problems solved quickly become skills. Problems unsolved become abandonment.
Check-ins
Follow up after training:
Week 1: "How's it going? Any obstacles?" Week 2: "What's working? What's not?" Week 4: "Ready for advanced techniques?"
Regular check-ins catch problems early.
Advanced Training
Once basics are solid:
- Deeper workflows
- Complex use cases
- Power user techniques
- Building custom approaches
Advanced training keeps engaged users growing.
Peer Learning
Create opportunities for users to teach each other:
- Success story sharing
- Tip exchanges
- Problem-solving sessions
- Peer mentoring
Teaching reinforces learning.
Measuring Training Effectiveness
During Training
Engagement indicators:
- Participation in exercises
- Questions asked
- Completion of activities
Immediate assessment:
- Can they complete the workflow?
- Do they understand when to use it?
- Are they confident to try?
After Training
Short-term (1-2 weeks):
- Are they using the tool?
- What questions are they asking?
- What obstacles are they hitting?
Medium-term (1-2 months):
- Is usage sustained?
- Are they finding new applications?
- Are they helping others?
Long-term (3+ months):
- Has the tool become habitual?
- Is performance improved?
- Are they advocates for AI?
Feedback Collection
Ask after each session:
- What was most valuable?
- What was confusing?
- What would you change?
- What do you need next?
Use feedback to improve future training.
Using AI to Improve AI Training
Creating Training Exercises
Create a hands-on training exercise for project managers
learning to use AI for contract review.
Requirements:
- Realistic scenario
- Clear learning objective
- Step-by-step instructions
- Verification checklist
- Approximate time: 15 minutes
Focus on identifying risk clauses in subcontract agreements.
Building Quick-Reference Guides
Create a one-page quick-reference guide for estimators
using AI for specification review.
Include:
- Top 5 workflows with example prompts
- Common mistakes to avoid
- Where to get help
- Verification reminder
Format for printing on one page, landscape orientation.
Developing FAQ Content
Based on these common questions from AI training sessions,
create a FAQ document:
Questions:
1. "What if the AI gives wrong information?"
2. "How do I know what to ask?"
3. "Can I trust AI for contract language?"
4. "Why doesn't it work on my PDFs?"
5. "How is this different from Google?"
Write clear, practical answers for construction professionals.
What's Next
Effective training builds individual skills. The next step is connecting those skills to team workflows and organizational processes—so AI becomes how your team works, not just a tool some people use sometimes.
TL;DR
- Train on workflows, not features—focus on work tasks AI helps accomplish
- Keep sessions short (15-20 minutes) and spread over time
- Make at least 50% of training time hands-on with real project materials
- Role-specific training beats generic training for everyone
- Support after training matters as much as the training itself
- Immediate application to real work is the biggest predictor of retention