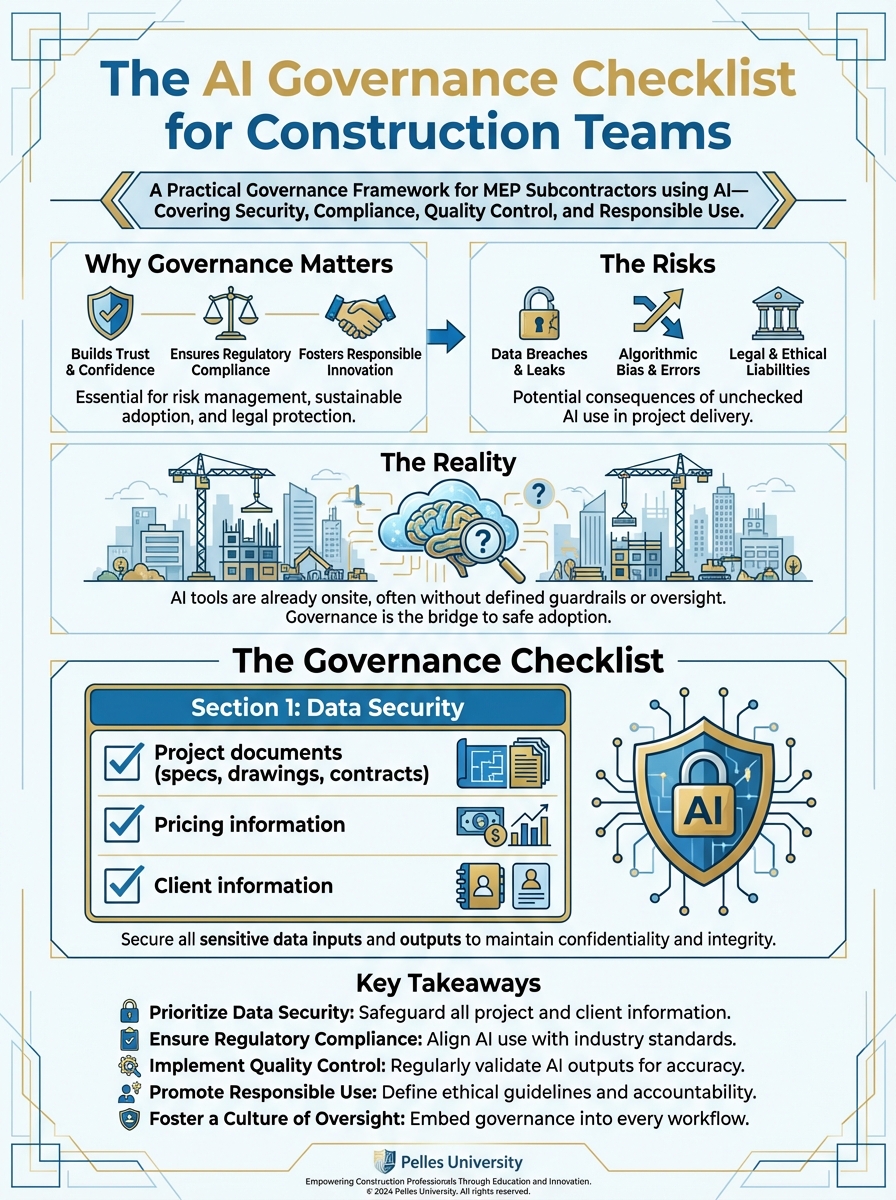
Your team is using AI. But do you know what data they're putting into it? Who's reviewing the outputs? What happens if something goes wrong?
AI governance sounds like big-company bureaucracy. But even small subcontractors need basic guardrails.
Here's a practical checklist for construction teams.
Why Governance Matters
The Risks
Data exposure: Confidential project information, pricing, client data—where does it go when you paste it into AI?
Quality failures: AI makes mistakes. Who catches them before they become expensive problems?
Compliance issues: Some contracts restrict AI use. Some clients prohibit it. Do you know what you've agreed to?
Liability questions: If AI-assisted work causes a problem, who's responsible?
The Reality
You're probably already using AI. The question isn't whether to allow it—it's how to manage it responsibly.
Good governance protects you without slowing you down.
The Governance Checklist
Section 1: Data Security
What data goes into AI tools?
- Project documents (specs, drawings, contracts)
- Pricing information
- Client information
- Employee information
- Financial data
For each data type, determine:
- Is this allowed?
- Are there restrictions?
- What's the sensitivity level?
Create clear guidelines:
| Data Type | AI Use Allowed? | Restrictions |
|---|---|---|
| Public specs | Yes | None |
| Client contracts | Limited | Redact pricing, remove client name |
| Internal pricing | Yes | Use tools with data protection |
| Employee data | No | Never upload to AI |
| Financial data | Limited | Aggregate only, no account numbers |
Tool selection criteria:
- What's the data retention policy?
- Is data used to train models?
- What security certifications exist?
- Where is data processed/stored?
- What happens if there's a breach?
Recommended practices:
- Use enterprise versions with data protection
- Avoid consumer/free tiers for sensitive data
- Review tool privacy policies
- Document which tools are approved
Section 2: Contract Compliance
Review your contracts:
- Do any contracts prohibit AI use?
- Do any require disclosure of AI use?
- Are there confidentiality clauses that affect AI?
- Are there technology clauses to review?
Common contract language to watch for:
Confidentiality provisions: "Contractor shall not disclose Confidential Information to any third party..."
AI tools may be considered a "third party" depending on interpretation.
Technology restrictions: "All work shall be performed by qualified personnel..."
Some clients interpret this to exclude AI assistance.
Data handling requirements: "All project data shall be stored only in approved systems..."
Cloud AI tools may not meet these requirements.
When you find restrictions:
- Document the requirement
- Communicate to affected team members
- Create project-specific guidelines
- Track compliance
Disclosure considerations:
- When is disclosure required?
- What level of disclosure is appropriate?
- Who needs to be informed?
- How is disclosure documented?
Section 3: Quality Control
Verification requirements:
- All AI outputs must be reviewed by qualified humans
- Critical items require additional verification
- Errors must be documented and addressed
- Patterns must be tracked and communicated
Define verification levels:
| Output Type | Verification Level | Verified By |
|---|---|---|
| Bid summaries | Standard | Estimator |
| Contract analysis | Enhanced | PM + Legal |
| Technical calcs | Enhanced | Engineer |
| Meeting notes | Standard | PM |
| Client communications | High | Manager approval |
Error handling:
- How are errors reported?
- Who investigates root causes?
- How are lessons shared?
- When does AI use stop for a process?
Quality metrics:
- Track error rates by process
- Monitor over time
- Set acceptable thresholds
- Review periodically
Section 4: Roles and Responsibilities
Define who does what:
AI Administrator:
- Manages tool access
- Maintains approved tool list
- Reviews new tool requests
- Monitors compliance
Process Owners:
- Define how AI is used in their process
- Create verification requirements
- Train team members
- Monitor quality
Users:
- Follow approved procedures
- Verify outputs
- Report errors
- Suggest improvements
Leadership:
- Set policy
- Allocate resources
- Review performance
- Make risk decisions
Section 5: Training Requirements
Before using AI:
- Tool-specific training completed
- Data security guidelines understood
- Verification requirements understood
- Error reporting process known
Training content:
- What AI can and cannot do
- How to write effective prompts
- When to verify vs. trust
- What data can be used
- How to report problems
Ongoing training:
- Updates when tools change
- Refreshers on policy
- Lessons learned sharing
- New process onboarding
Section 6: Incident Response
If something goes wrong:
Data exposure:
- Identify what was exposed
- Assess potential impact
- Notify affected parties if required
- Document incident
- Implement prevention measures
Quality failure:
- Identify the error
- Assess impact (was work affected?)
- Correct the work
- Document the failure
- Adjust process to prevent recurrence
Compliance violation:
- Identify the violation
- Assess contract/legal implications
- Notify appropriate parties
- Remediate if possible
- Adjust controls to prevent recurrence
Incident documentation:
- Date and time
- What happened
- How it was discovered
- Impact assessment
- Actions taken
- Prevention measures
- Lessons learned
Section 7: Policy Documentation
Document your policies:
AI Use Policy:
- Scope (who, what, when)
- Approved tools
- Data handling rules
- Verification requirements
- Training requirements
- Compliance obligations
Keep it simple:
- One page if possible
- Clear dos and don'ts
- Examples of acceptable use
- Examples of prohibited use
- Where to get help
Communication:
- Policy distributed to all employees
- New employees receive during onboarding
- Annual review and acknowledgment
- Updates communicated promptly
Section 8: Regular Review
Monthly:
- Review any incidents
- Check tool usage patterns
- Address emerging issues
Quarterly:
- Review quality metrics
- Assess new tool requests
- Update training as needed
- Review contract requirements
Annually:
- Full policy review
- Technology assessment
- Risk assessment update
- Training program refresh
Implementation Approach
Start Simple
Don't try to implement everything at once:
Week 1: Data security basics
- Identify what data goes into AI
- Set clear restrictions
- Communicate to team
Week 2: Quality control
- Define verification requirements
- Set up error tracking
- Assign responsibilities
Week 3: Documentation
- Write simple policy
- Distribute to team
- Get acknowledgments
Week 4: Review and adjust
- Address questions
- Refine based on feedback
- Plan ongoing reviews
Scale Appropriately
5-person team: One-page policy, informal processes 25-person team: Documented policy, assigned roles 100-person team: Formal program, dedicated oversight
Match governance to your size and risk.
Common Questions
"Does this apply to personal use?"
If employees use personal AI tools for work tasks, the same data security concerns apply. Either allow it with guidelines or prohibit it and provide company tools.
"What about AI in other software?"
Many tools now include AI features. Apply the same data security and quality control principles regardless of where AI appears.
"How do we enforce this?"
Start with training and communication. Most people will follow reasonable guidelines if they understand the reasons. Address exceptions when they arise.
"What if a client asks about our AI use?"
Be prepared to explain:
- What tools you use
- What data goes into them
- What quality controls exist
- How you verify outputs
Transparency builds trust.
What's Next
Governance protects your company as you adopt AI. The foundation is in place. Now it's time to start using these tools effectively—beginning with the specific workflows that will have the most impact on your business.
TL;DR
- AI governance isn't just for big companies—every contractor needs basic guardrails
- Focus on four areas: data security, contract compliance, quality control, and roles
- Document simple policies—one page is better than none
- Train everyone before they use AI tools
- Review regularly and adjust based on what you learn