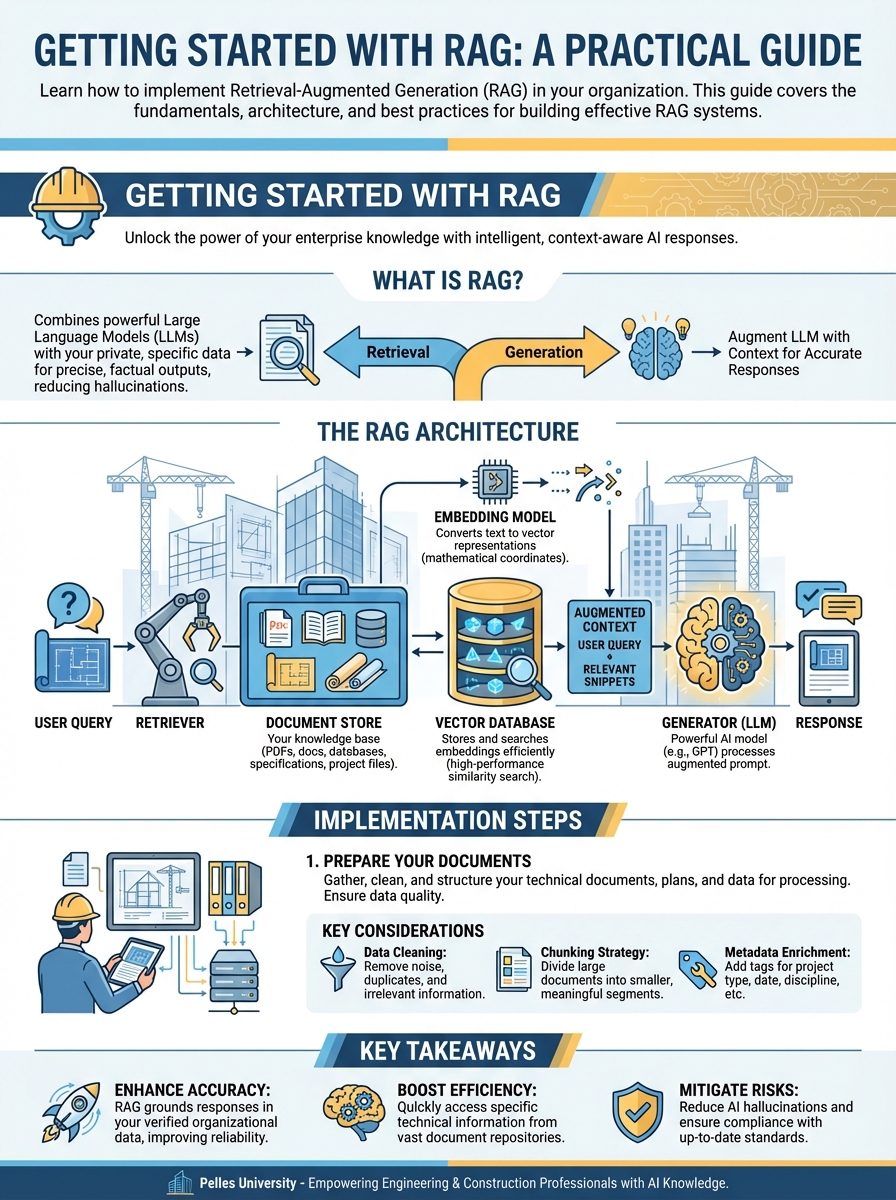
Getting Started with RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become one of the most practical ways to enhance Large Language Models (LLMs) with your organization's specific knowledge. Unlike fine-tuning, RAG allows you to keep your data up-to-date and maintain control over what information the model can access.
What is RAG?
RAG combines two powerful capabilities:
- Retrieval: Finding relevant documents from your knowledge base
- Generation: Using an LLM to generate answers based on those documents
This approach solves many of the limitations of traditional LLMs, including hallucinations and outdated information.
The RAG Architecture
A typical RAG system consists of:
- Document Store: Your knowledge base (PDFs, docs, databases)
- Embedding Model: Converts text to vector representations
- Vector Database: Stores and searches embeddings efficiently
- LLM: Generates responses based on retrieved context
Implementation Steps
1. Prepare Your Documents
Start by gathering and cleaning your source documents. This includes:
- Removing irrelevant content
- Splitting into appropriate chunks
- Adding metadata for filtering
2. Create Embeddings
Use an embedding model to convert your documents into vectors:
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
response = client.embeddings.create(
input="Your document text here",
model="text-embedding-3-small"
)
3. Store in Vector Database
Popular options include Pinecone, Weaviate, and Chroma. Choose based on your scale and requirements.
4. Build the Query Pipeline
When a user asks a question:
- Convert the question to an embedding
- Search for similar documents
- Pass documents + question to the LLM
- Return the generated answer
Best Practices
- Chunk size matters: Experiment with different sizes (500-1500 tokens)
- Use metadata filtering: Improve relevance with category/date filters
- Implement reranking: Add a reranking step for better results
- Monitor and iterate: Track which queries fail and improve
Common Pitfalls
- Too large chunks: Dilute relevance and waste context
- Ignoring preprocessing: Garbage in, garbage out
- No evaluation: Build metrics to measure quality
Next Steps
Ready to implement RAG in your organization? Consider starting with a pilot project focused on a specific use case, such as internal documentation search or customer support.